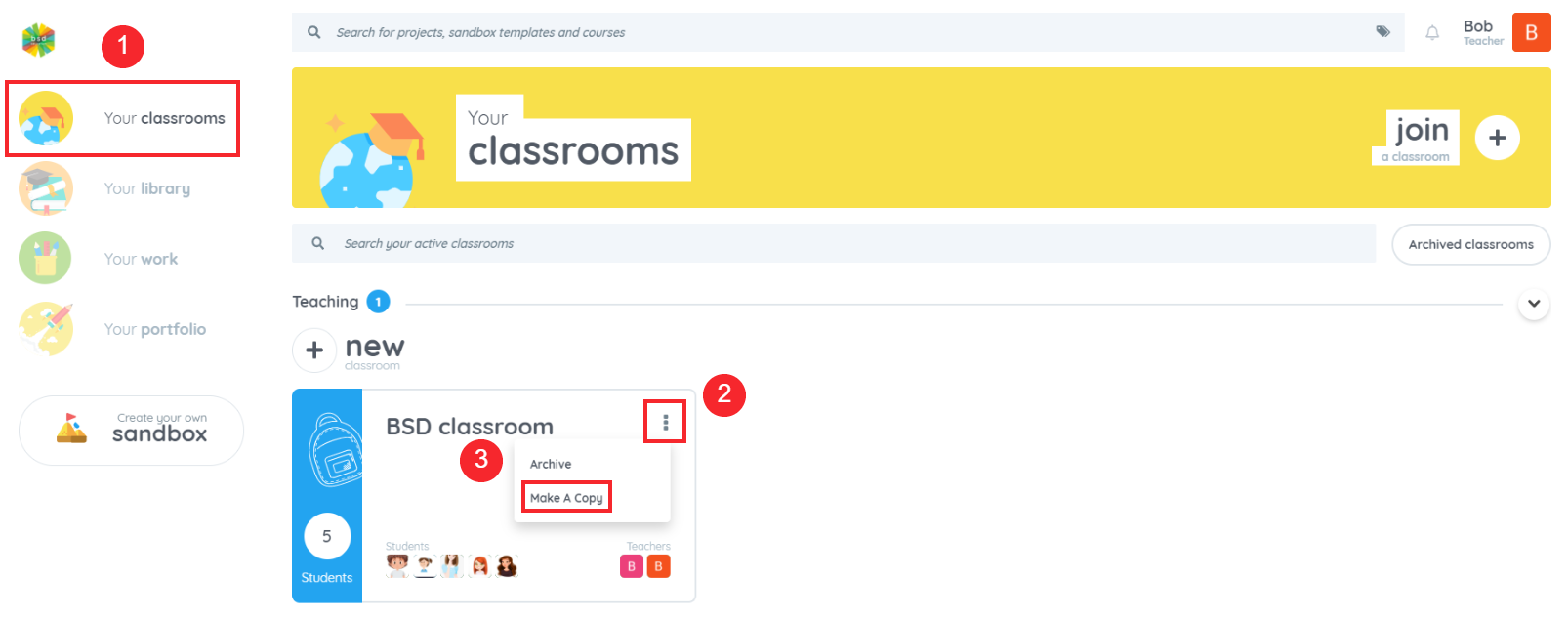
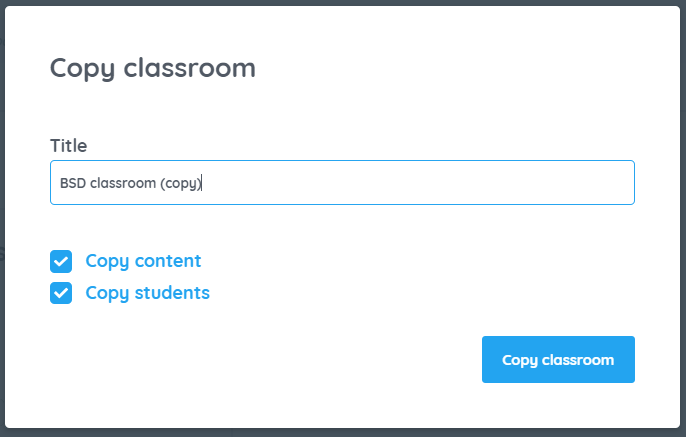
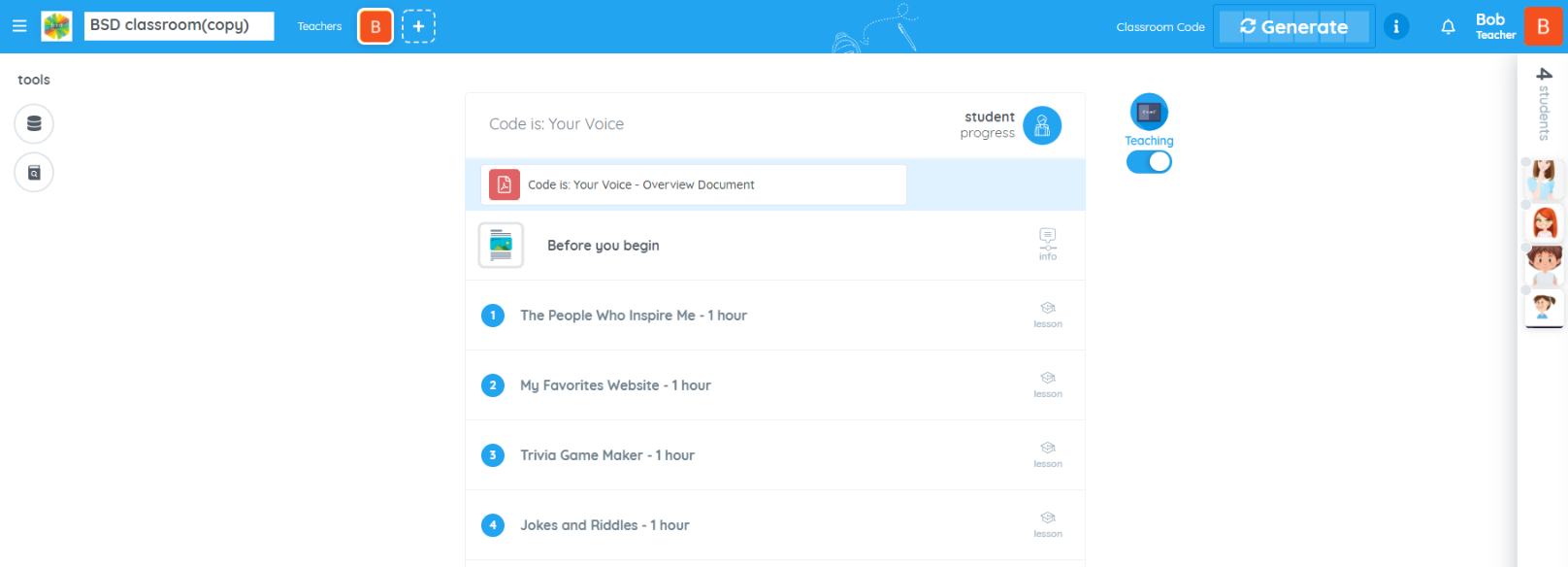
In the rapidly evolving landscape of education, it’s becoming increasingly evident that preparing students for the future requires more than just traditional subjects like math, science, and language arts. As technology continues to permeate every aspect of our lives, there’s a growing consensus among educators about the importance of integrating computer science, computational thinking, and design thinking into the K-12 core curriculum. By doing so, we not only equip students with essential skills for the future but also foster a mindset of innovation, problem-solving, and collaboration.
Computer science, once considered a niche subject, has now emerged as a fundamental literacy in the digital age. It’s not just about coding; it’s about understanding algorithms, data structures, and computational processes. By introducing computer science concepts early on, we empower students to become creators rather than mere consumers of technology. Whether it’s learning to code with BSD Education or exploring robotics through hands-on projects, students develop critical thinking skills and gain a deeper understanding of how technology works.
However, computer science alone is not sufficient. Enter computational thinking – a problem-solving methodology rooted in the principles of computer science. It involves breaking down complex problems into smaller, more manageable parts, identifying patterns, and devising algorithms to solve them. Computational thinking transcends the boundaries of programming and can be applied across various disciplines. From analyzing historical data to optimizing logistical processes, students learn to approach challenges systematically and analytically. By integrating computational thinking into the core curriculum, we cultivate a mindset that is essential for success in the digital age.
But solving problems is only half the battle. Design thinking complements computational thinking by emphasizing empathy, creativity, and iterative prototyping. Originating from the world of product design, design thinking provides a human-centered approach to problem-solving. Students are encouraged to empathize with end-users, brainstorm innovative solutions, and test prototypes through rapid experimentation. By incorporating design thinking into the curriculum, we foster a culture of innovation where students learn to tackle real-world problems with empathy and creativity.
Now, the question arises – how can teachers integrate these concepts into their existing curriculum? The key lies in interdisciplinary connections and project-based learning. Instead of treating computer science, computational thinking, and design thinking as separate subjects, teachers can look for opportunities to integrate them into existing lessons.
For example, a history class could explore the impact of algorithms on historical events, a science class could analyze data using computational thinking principles, and an art class could incorporate design thinking into the creative process.
Language Arts: Students can analyze language patterns and structures using computational thinking concepts such as algorithms and loops. They could also use design thinking to create multimedia presentations or websites for their writing projects.
Mathematics: Teachers can incorporate computer science concepts by having students create algorithms for solving mathematical problems or exploring the mathematics behind coding algorithms. Additionally, design thinking can be applied to create visually appealing and user-friendly mathematical models or visualizations.
Physical Education: Students can apply computational thinking by designing algorithms for optimizing workout routines or analyzing sports data. Design thinking can be integrated by having students redesign sports equipment or create innovative fitness apps.
Social Studies: Computational thinking can be utilized to analyze large datasets related to historical events or societal trends. Students can also apply design thinking principles to propose solutions to contemporary social issues or design informative infographics about historical events.
Foreign Language: Computational thinking can be applied to language learning through the creation of algorithms for language translation or language learning apps. Design thinking can be used to design immersive language learning experiences or culturally relevant multimedia projects.
Music: Students can explore computational thinking through the creation of algorithms for composing music or analyzing musical patterns. Design thinking can be integrated by having students design innovative musical instruments or create visually engaging music videos.
Career and Technical Education (CTE): Students can apply computational thinking to solve real-world problems in their chosen career pathways, such as engineering, healthcare, or business. Design thinking can be used to develop prototypes or design solutions to industry-related challenges.
Environmental Science: Computational thinking can be utilized to analyze environmental data and model environmental processes. Design thinking can be applied to create sustainable solutions to environmental challenges or design eco-friendly products.
By integrating computer science, computational thinking, and design thinking across various subjects, teachers can provide students with interdisciplinary learning experiences that foster critical thinking, creativity, and problem-solving skills. It’s not just about preparing students for jobs in the tech industry; it’s about equipping them with essential skills and mindsets for success in an increasingly complex and interconnected world. By embracing interdisciplinary connections and project-based learning, teachers can empower students to become lifelong learners, critical thinkers, and innovative problem-solvers. As we navigate the challenges and opportunities of the future, this pedagogical imperative has never been more urgent or relevant.